IoT (Internet of Things)
Reach out and start everything
IoT is an emerging paradigm of Internet connected things that allow the physical objects or things to connect, interact and communicate with one another similar to the way humans talk through the web in today’s environment. It connects systems, sensors and actuator instruments to the broader Internet. The applications of IoT are not limited to particular fields, but span a wide range of applications such as energy systems, homes, industries, cities, logistics, health, agriculture, and so on.
The goal of IoT is not only just connecting things such as machines, devices and appliances, but also allowing the things to communicate, exchanging control data and other necessary information while executing applications.
It consists of IoT devices that have unique identities and are capable of performing remote sensing, monitoring and actuating tasks. These devices are capable of interacting with one another directly or indirectly. Data collection is performed locally or remotely via centralized servers or cloud based applications. These devices may be data collection devices to which various sensors are attached such as temperature, humidity, light, etc., or they may be data actuating devices to which actuators are connected, such as relays.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is also affecting the industrial sector, especially for industrial automation systems in which internet infrastructure provides extensive access to sensors, controls and actuators, with a goal of increasing efficiency.
Application & Solutions of IoT:
The major area where IoT deals with energy management systems is the smart grid. IoT extends the benefits of smart grid beyond the automation, distribution and monitoring being done by the utilities.
IoT increased the use of wireless technology to connect power industry assets and infrastructure in order to lower the power consumption and cost. Some of the examples of IoT usage include SCADA, smart metering, building automation, smart grid, and connected public lighting.
IoT based SCADA
SCADA is one of the major application areas of IoT. SCADA allows the centralized monitoring and control of remote located generation and transmission systems. It consists of sensors, actuators, controllers and communication devices at the remote field place, and central master unit with communication systems at the controlling side. It collects the data from sensors in the field and provides a user interface in HMI at central station. Also, it stores the time-stamped data for later analysis.
IoT SCADA is a step beyond SCADA that has been in use from earlier days. It provides real-time signal acquisition and data logging through IoT servers and internet technologies. It integrates the individual devices, machines, sensors and other electrical equipment with internet by realizing the functionality of supervision and control.

IoT based Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) is an integrated system of smart meters, communications networks, and data management systems that enables two-way communication between utilities and customers. Customer systems include in-home displays, home area networks, energy management systems, and other customer-side-of-the-meter equipment that enable smart grid functions in residential, commercial, and industrial facilities.
Smart metering is an essential element in smart grid implementations as they are using Internet of Things technologies to transform traditional energy infrastructure. Smart metering through IoT helps to reduce operating costs by managing metering operations remotely. It also improves the forecasting and reduces energy theft and loss. These meters simply capture the data and send it back to the utility companies over highly reliable communication infrastructure.
Building Automation
IoT based solutions enable the efficient way of monitor and control of buildings to property owners as they connect lighting systems, elevators, environmental systems and other electrical appliances with internet and communication technologies. It saves the power consumption by automatically turning off the lights when rooms are not occupied and also by making sure of not drawing too much power by appliances. IoT based appliances provide remote monitoring and control through mobile and web applications to the end users or owners.
Data collected with IoT helps in analytics and energy management systems. With the help of IoT, the installation, monitoring, and control of building automation and control systems becomes an easy and manageable task, finds the report.

IoT based Connected Public Lighting
Outdoor lighting is among the most significant and expensive infrastructure assets owned by municipalities and utilities, often consuming up to half of a city’s total energy budget.
This is the part of a project under smart cities where wireless IoT solutions are deployed to connect IP based lights. This smart public lighting uses intelligent-connected outdoor LED luminaries which are centrally controlled from the control station. This type of infrastructure also facilitates dynamical adjustment of illumination based on environmental changing conditions. This would dramatically result lower operating costs and power consumption.
By centrally monitoring and controlling an intelligent network of outdoor LEDs, we can:
- Adjust lighting dynamically, for example, adding or reducing illumination at different times of day or in response to weather events
- Improve safety by detecting outages faster, and increasing lighting in higher-crime areas or in response to emergencies
- Dramatically lower power consumption and costs, with some cities realizing up to 80% energy savings
IoT based Smart Grid
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) is a key part of the smart grid and there are millions of smart meters already connected to the grid. Smart grid makes better use of available energy supply by optimizing electricity generation and distribution depending upon the load demand.
This includes Ethernet based communication connected substations with intelligent equipment devices at each substation. This enables the automation of substations which can be coordinated effectively for a better power distribution especially during peak hours.
In the perspective of energy saving, smart grid is an excellent solution to optimize the energy consumption while the IoT can be a solution that offers consumers the convenience of having a real-time method to control and monitor energy usage in a home.
Increased intelligence and automation in smart grid results in many heterogeneous applications benefiting from the Internet of Things, such as demand response, energy delivery efficiency/reliability, and fault recovery. However, vulnerabilities in smart grid arise due to public communication infrastructure and Internet-based protocols. To deal with security threats, energy big data should be thoughtfully stored and processed to extract critical information and security and blackout warnings should be given in an early stage.

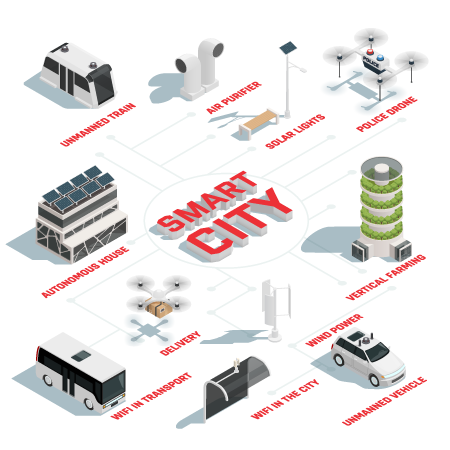
IoT based Smart City Solutions
More and more cities around the world are transitioning towards being called “Smart Cities.” These cities are integrating sensors and various monitoring devices through a network, typically the internet, in an effort to optimize city operation and service efficiency along with improving their interface with citizens directly. The data that is collected can be analyzed to manage many municipal assets such as power plants, water and sewage systems, traffic and transportation systems, and many other community services. In essence, smart cities use the IoT to collect data and analyze it in order to directly interact with city infrastructure and to monitor real-time city assets and community evolution in order to improve operating efficiency and to proactively react to potential problems before they arise.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is making it possible to make cities greener, safer and more efficient. By connecting devices, vehicles and infrastructure everywhere in a city, governments and their partners can reduce energy and water consumption, keep people moving efficiently, and improve safety and quality of life.
Cities that are livable, resilient and sustainable are most important for a continued existence of humans on the planet. And technology will play a key role in making urban living smart and sustainable. Our innovation and technology is enabling such efforts for bringing comfort, security, resource optimization into urban living and making the interface between citizens and government seamless.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Solutions
IoT incorporates functions that enable the users to connect all objects with internet. Its basic functioning is to capture and communicate data with M2M communication, sensor data and automation technologies. It is transpired to be a strong economic driver over the next decade. The use of IoT technologies in the industry is ever increasing as it minimizes manual effort and increases efficiency.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) collects data from connected devices (i.e., smart connected devices and machines) in the field or plant and then processes this data using sophisticated software and networking tools. The entire IIoT requires a collection of hardware, software, communications and networking technologies.
With our team of experts in this field, we deliver you innovative industrial monitoring with portable sensors that allow you to access data at all times.
We provide smart sensors that are integral enablers in Industrial IoT. The key functions of our sensors are to identify and locate items, determine the environmental conditions, etc.


Enterprise IoT Solutions
Enterprise Internet of Things is the next advancement in technology that enables physical ‘things’ with embedded computing devices (tiny computers) to participate in business processes for reducing manual work and increasing overall business efficiency. Taking advantage of a combination of technologies ranging from embedded devices with sensors and actuators to internet based communication and cloud platforms, the enterprise IoT applications can now automate business processes that depend on contextual information provided by programmed devices such as machines, vehicles and other equipment.
Further such enterprise IoT applications can also send control instructions to these devices based on specific business rules. The Internet of Things, or IoT, is an exciting new concept, allowing previously unconnected physical devices to connect to the internet; the Internet of Things will ultimately become as fundamental as the Internet itself, with lots of opportunities and trials along the way. Enterprise IoT is anticipated to enhance enterprise efficiency, facilitate new business models, and align physical operations with digital assets on a real-time basis. Cloud and Big Data technology support Enterprise Internet of Things further as they provide scalability and intelligent insights. The goal is to generate insights, allowing for faster, accurate and appropriate decision making, and fostering a more customer centric business.
